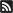look what we did!
Category: Innovation Bonds
Biocompatibility Makes Polyurethane Work in Medical Devices
It may surprise you to learn that polyurethanes are commonly used in short-term implants and other medical devices that need to be compatible with the human body.
The reason is that TPUs — also known as polyurethane elastomers — have a molecular structure that’s very similar to that of human proteins. As a result, they can be used to mimic certain bodily functions without causing the same level of blood coagulation that is caused by other materials. That helps in preventing dangerous blood clots from forming. They are also often softer than other materials, which can make them more comfortable for patients.
In addition to biocompatibility, polyurethanes bring other desirable traits to medical implants, including durability, adhesion, strength and tear and abrasion resistance. They have been used in applications that include artificial heart and pacemakers, artificial dialysis cylinders and for indwelling catheters and for vascular access.
On the outside, polyurethane’s water resistance and breathability make it well suited for advanced wound dressings. So-called “interactive” dressings made from semi-permeable polyurethane films keep the wound moist, which aids in the healing process because they are permeable to water vapor. However, they also fight infection because they resist bacterial breach.